Objective
To investigate the in vitro effects of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) on human osteoarthritic chondrocytes.
Design
Chondrocytes isolated from human osteoarthritic knee cartilage were three-dimensionally cultured in alginate beads, except for cell proliferation experiment. Cells were treated with DHEA in the presence or absence of IL-1beta. The effects on chondrocytes were analyzed using a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxy-phenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium inner salt (MTS) assay (for chondrocyte proliferation), a dimethylmethylene blue (DMB) assay (for glycosaminoglycan (GAG) synthesis), and an indole assay (for DNA amount). Gene expressions of type I and II collagen, metalloproteinase-1 and -3 (MMP-1 and -3), and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) as well as the IL-1beta-induced gene expressions of MMP-1 and -3 were analyzed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The protein synthesis of MMP-1 and -3 and TIMP-1 was determined by Western blotting.
Results
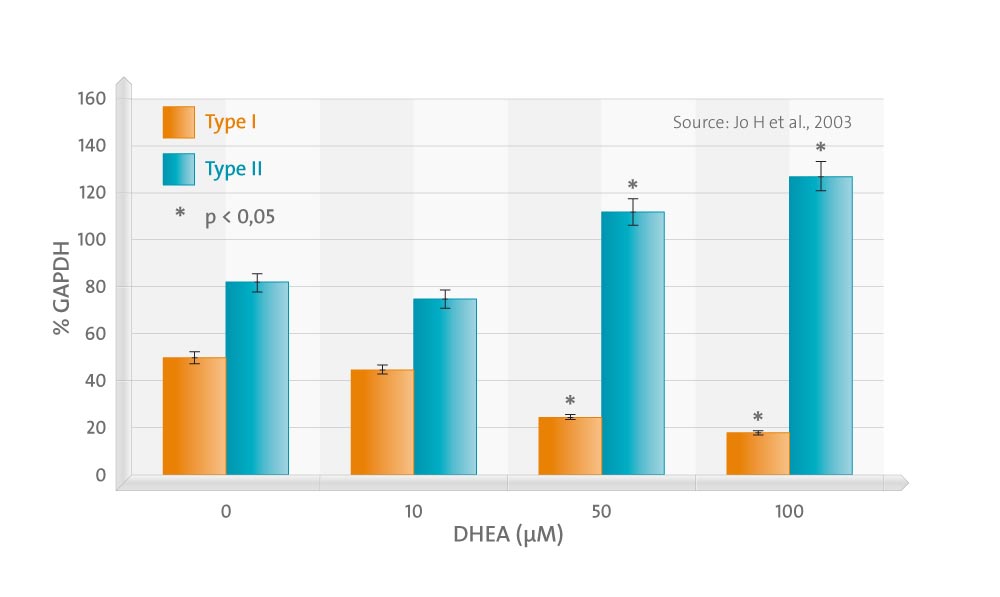
The treatment of chondrocytes with DHEA did not affect chondrocyte proliferation or GAG synthesis up to 100 micro M of concentration. The gene expression of type II collagen increased in a dose-dependent manner, while that of type I decreased. DHEA suppressed the expression of MMP-1 significantly at concentrations exceeding 50 micro M. The gene expression of MMP-3 was also suppressed, but this was without statistical significance. The expression of TIMP-1 was significantly increased by DHEA at concentrations exceeding 10 micro M. The effects of DHEA on the gene expressions of MMP-1 and -3 were more prominent in the presence of IL-1beta, in which DHEA suppressed not only MMP-1, but also MMP-3 at the lower concentrations, 10 and 50 micro M, respectively. Western blotting results were in agreement with RT-PCR, which indicates that DHEA acts at the gene transcription level.
Conclusions
Our study demonstrates that DHEA has no toxic effect on chondrocytes up to 100 micro M of concentration and has an ability to modulate the imbalance between MMPs and TIMP-1 during OA at the transcription level, which suggest that it has a protective role against articular cartilage loss.